🟡 Self-Consistency
Self-consistency1 is a follow up to CoT that generates multiple chains of thought instead of just one, then takes the majority answer as the final answer.
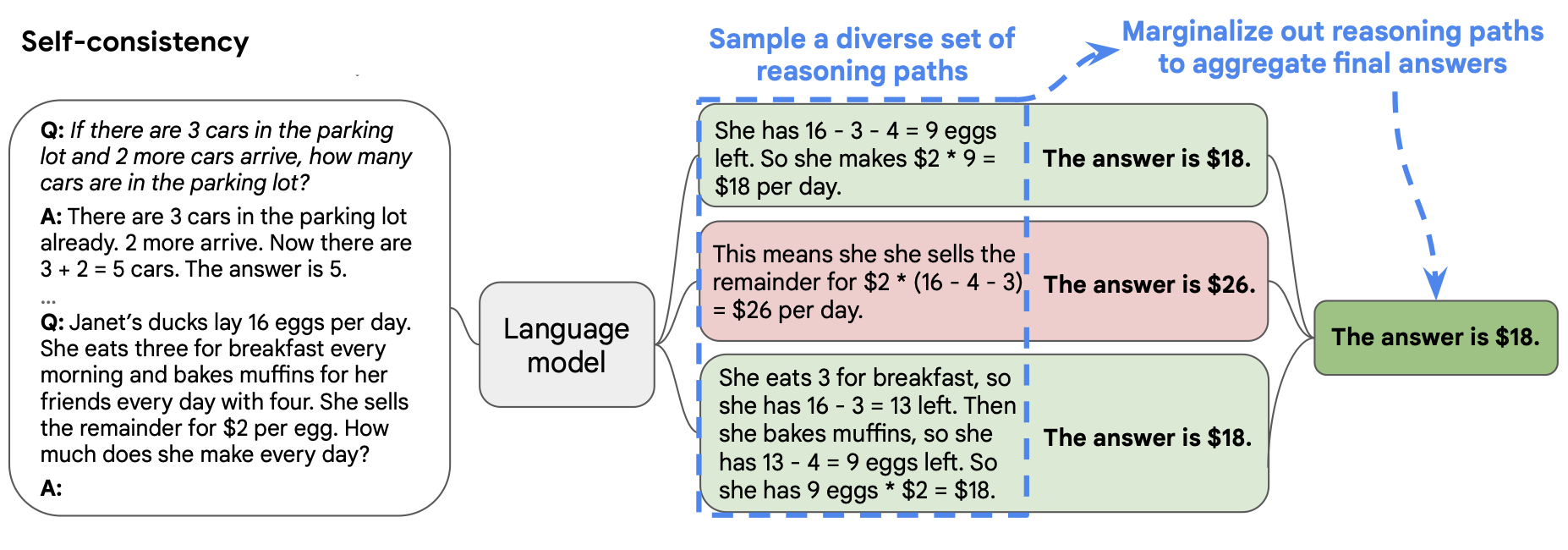
In the below figure, the prompt on the left is written using the Few-Shot-CoT paradigm. Using this one prompt, multiple chains of thought are generated independently. Answers are extracted from each and the final answer is computed by "marginalizing out reasoning paths". In practice, this just means taking the majority answer.
Results
Self-consistency has been shown to improve results on arithmetic, commonsense and symbolic reasoning tasks.
Even when regular CoT was found to be ineffective2, self-consistency was still able to improve results.
Notes
Wang et al. discuss a more complex method for marginalizing out reasoning paths, which deals with the LLM generated probabilities for each chain of thought. However, they do not use this method in their experiments, and majority voting seems to usually have the same or better performance regardless.